|
|
Module 3: Knowledge management in-house and across organisations. |
|
|
Prof. Marina Dabić, Tena Obradović Posinković |
|
|
For the successful implementation of open innovation activities, it is not enough for SMEs to cooperate with external partners and exchange their ideas, technology, and knowledge. Small and medium-sized enterprises also need to develop capabilities, enable their employees to acquire knowledge and manage existing and newly acquired knowledge. Knowledge management helps managers control knowledge within their organizations, but also knowledge available outside their companies. In this module SMEs from bioeconomy and agri-food industry can learn about the types of knowledge, but also get advice for managing in-house knowledge, as well as knowledge across organizations. |
|
Upon completing this module, you should be able to: |
|
Knowledge management challenges in SMEs
Knowledge management helps companies to collect, distribute and use information more effectively. It also allows companies to achieve their strategic goals, to create value and to improve their businesses. In today’s economy, activities related to knowledge management play an important role in maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage[8]. In dynamic environments, if SMEs want to survive, they need to innovate and create new products and services. The success of an SME depends on type of strategic partner, their collaboration and ecosystem. Unlike large companies, which have entire knowledge management departments, SMEs have limited resources and knowledge is often concentrated in a few key individuals. Therefore, SMEs in bioeconomy and agri-food industry are encouraged to collaborate with external partners because there is a greater chance of success if SMEs are part of ecosystem. For the successful implementation of knowledge management, SMEs need to create an open culture that will encourage further adoption of open innovation practices[9].
Open innovation activities, both inbound and outbound, can help companies to either sell or buy knowledge. This type of collaboration allows SMEs to use external knowledge more effectively than the knowledge that the firm could produce by investing in its own research and development[10]. The OI paradigm transformed the new product development process into a more knowledge-intensive activity. What is more, successful knowledge management helps companies to lower their prices, to improve the quality of their products but it also helps SMEs to meet customer demands. KM can help companies to improve their capabilities and skills and to transform information into valuable data. It can also help companies to reduce a risk of product failure.
Furthermore, new advanced technologies (big data, artificial intelligence, internet of things) enable SME to improve their production. Advanced technologies allow collection of information and transformation into meaningful data. In this way, SME can shorten time to market, make products more customer-oriented, speed up production and reduce production costs. Companies can only truly benefit from digital transformation if they improve their knowledge management[11]. Improving their knowledge management will enable companies to find and use the right information necessary for the success of their business, as well as develop a more sophisticated use of that knowledge. Digital transformation mechanisms positively influence the implementation of knowledge management and enable transparency[12].
SMEs are facing internal and external challenges in knowledge management. From external perspective, fast market changes, wars, pandemics, natural disasters, increasing cost of raw materials and others may affect SMEs businesses. On the other hand, limited resources, talents, knowledge, or even employees fear of sharing knowledge may enable SMEs to produce new products and services. Since the main challenge of most SMEs is often the scarcity of resources, the open strategy to innovation represents a great opportunity for SMEs businesses. Unlike large companies, small and medium-sized companies can make decisions much faster because their decision-making process is mostly carried out by one or several people. What is more, SME have simple organizational structure, thus, knowledge management can be organized in more efficient way than in large companies with more sophisticated structure. In SMEs, employees can communicate much faster and easier, also the bureaucracy is reduced to a minimum which encourages employees to be more open and to share their ideas.
11 key factors for successful implementation of knowledge management in SMEs are proposed[13]:
- Management leadership and support is one of the key factors for successful implementation of knowledge management into SMEs. Leaders can set a good example for their employees. If leaders are willing to share their ideas with others, if they are open and not afraid to seek knowledge outside their company, there is a greater chance that employees will behave in the same way.
- Culture defines norms, core values and the way employees will behave in every organization. If a company fosters a culture of openness, if employees are willing to share their ideas and are not afraid of failure, the exchange of knowledge is more likely to result in new products or services. Furthermore, if a company shares its ideas and knowledge with external partners and fosters a collaborative culture, it can benefit from implementing open innovation activities.
- Information technology enables the connection between people and information. It helps companies find information, knowledge, and partners faster. At the time of digital transformation, advanced technologies (for example big data, Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and others), IT can help small and medium-sized enterprises to collect information faster and turn it into valuable data.
- Strategy and purpose are key factors for successful implementation of knowledge management. Small and medium-sized enterprises should have a clear vision and strategy to achieve their business goals. Also, this strategy should be clear to all employees.
- Measurement is important to understand whether knowledge management has been successfully implemented or not. It is important to measure the value of knowledge management so that managers, employees, and stakeholders can assess whether all activities have been successful. Measurement is a very important activity, but it is still not entirely clear how the success of knowledge management can be measured.
- Organizational infrastructure enables SMEs to define roles and teams that will be responsible for knowledge management activities. It is important for a company to have employees with specific knowledge (for example, a chief knowledge officer) in order to implement knowledge management successfully.
- Processes and activities empower SMEs to collect, transform and use knowledge. Furthermore, for the successful implementation of knowledge management, it is important that the process is organized in a systematic way and that the process itself as well as the activities are clear to the employees.
- Motivational aids enable SMEs to motivate their employees to practice knowledge management and to share and use knowledge. Managers should provide incentives to employees to create a culture for effective knowledge management. The reward system should be based on teamwork, employees’ willingness to share and apply knowledge or creative solutions.
- Resources play an important role in knowledge management in SMEs. The main concern of every company is whether they have the available resources necessary for new product development. Therefore, resources in terms of employees, time, financial resources, technological resources must be well distributed and timely available in order for SMEs to implement knowledge management in an efficient manner.
- Training and education are important for small and medium-sized companies because they enable employees to recognize knowledge as an important resource needed for successful knowledge management. Managers should provide training for employees to help them understand and learn about knowledge management. Training and education will create new skills, abilities and enable employees to perform better in new knowledge-oriented activities.
- Human resource management is important for managing both knowledge and people. Proper HRM will enable the recruitment of good employees, will enable the development of each employee as well as the development of his skills and abilities, and strive to retain employees. HRM is responsible for attracting employees with the necessary knowledge and competences to the organization.
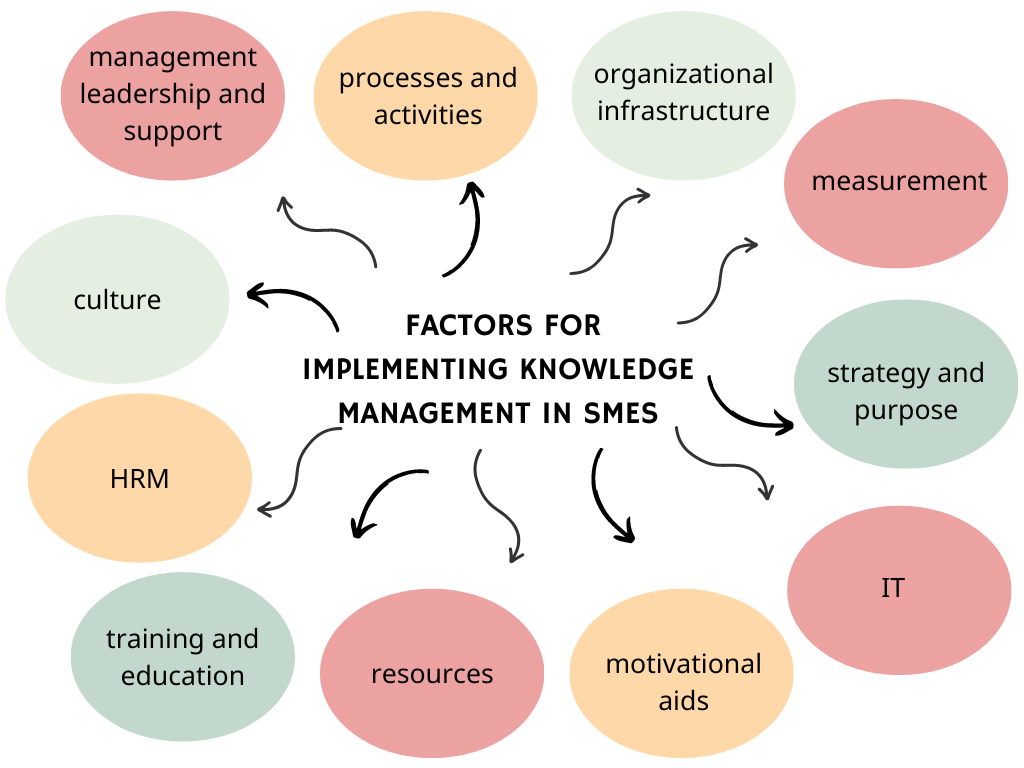
Figure 3: Choosing the right partner[14]
Source: Wong, K. Y. (2005). Critical success factors for implementing knowledge management in small and medium enterprises. Industrial management & Data systems, 105(3), 261-279. p. 266-267. https://doi.org/10.1108/02635570510590101
Both academics and practitioners could benefit from understanding critical success factors for knowledge management in SMEs[15].
Take a 3-5 minutes and think:
5. What do you think are the critical success factors for implementing knowledge management in your SME?
Think how could you explain these terms to another person and write it down.